Services
MVNO Traffic Modes
- Interconnection between MVNO and other networks
- Call origination
MVNO's originating traffic can take place in two alternative ways:
- Traffic through its own point of interconnection (based on definition of MVNO) or
- Traffic through the point of interconnection of its hosting MNO (based on the definition of ESP)
Traffic through the point of interconnection of an MVNO
Outgoing traffic from MVNO's subscribers goes through MNO's Base Station (BTS) and Base Station Controller (BSC) to MVNO's mobile switch (MSC). Based on the information collected from MVNO's Visiting Location Register (VLR), call is routed to MVNO's MSC and the Home Location Register. Based on the information recorded in the HLR, call is then routed by the MVNO to other networks, figure 2.
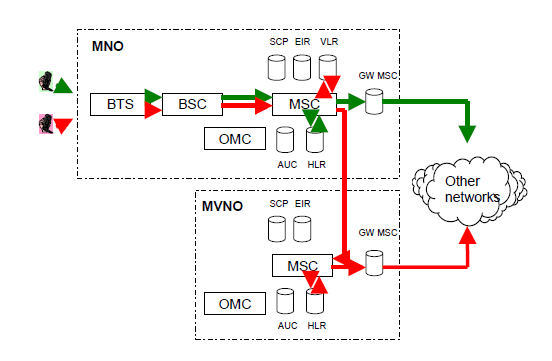
Fig 2. MNO's and MVNO's outgoing traffic to other networks through the point of interconnection.
The cost of MVNO's call origination is comparable with the cost of call origination of the hosting MNO. Taking into account of MVNO's cost of MSC and related equipment, the cost of MVNO call origination can be slightly higher than the cost of MVNO's call origination can be slightly higher than the cost of MNO's call origination. It is to be noted, however, that the difference may be marginal. Most costs are born from radio access infrastructure, base stations, base station controllers and transmission.
Outgoing traffic through the point of interconnection of the hosting MNO
Another alternative for MVNO outgoing traffic is to route it through the point of interconnection of the MNO, figures 3 and 4. Functionally MVNO differs from other MNO's service providers only with regard the service level and scope. By definition, lacking interconnection .ink of its own makes MVNO an ESP, not a real MVNO.
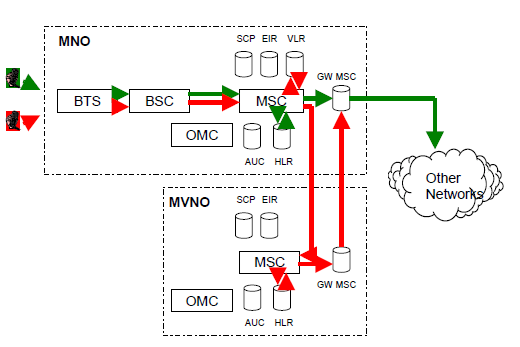
Figure 3 MVNO's outgoing traffic via its own MSC and the point of interconnection of the hosting MNO.
MVNOs outgoing traffic can also be routed out directly from MNO's MSC, figure 4. Updating MNVO's MSC takes place with signalling. In this alternative, the use of MVNO's own IN platform is limited.
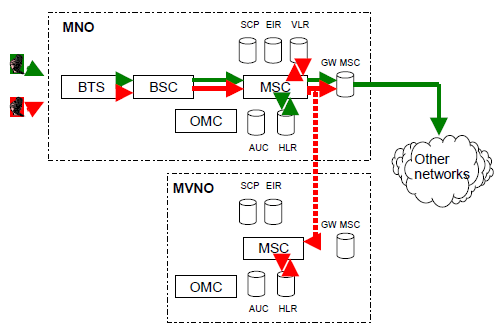
Figure 4 MVNO's outgoing traffic directly from the hosting MNO.
Call termination
Also terminating traffic to MVNO can be routed in two alternative ways:
- Via MVNO's own point of interconnection or
- Via MNO's point of interconnection.
Call termination through MVNO's own point of interconnection
A call to MVNO's network is routed via its own point of interconnection. Call is routed to MVNO's MSC and Home Location Register. Based on the information recorded in the Home Location Register, call is routed to MVNO's subscribers through MNO's radio infrastructure, figure 5.
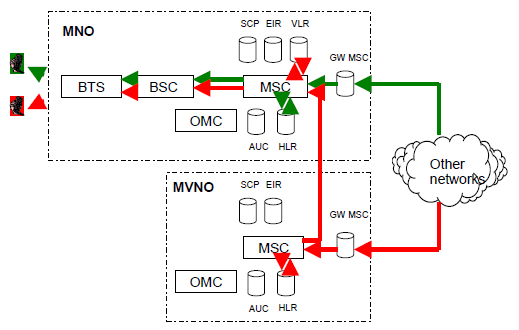
Figure 5: MNO's and MVNO's call termination via their own interconnection links.
Similar to call origination, the cost of call termination in the MVNO's network may be slightly higher than the call termination in the MNO's network, because of some parallel network components (MSC, for example). Difference is marginal, however, taking into account that the bulk of total costs are born by the radio infrastructure (BTS, BSC and transmission links).
Call termination through the interconnection point of the hosting MNO
A call to MVNO's subscriber can be routed via the gateway MSC of the hosting MNO, figure 6. From MNO's MSC call is routed to MVNO's mobile switch MSC, to its HLR and then through MNO's radio access to the MVNO's subscribers. MVNO is tied with MNO's interconnection link and –prices. A call can also be routed to MVNO's subscriber directly from the MSC of the hosting MNO, figure 7.
In both alternatives, MVNO is tied with the interconnection of the hosting MNO. Functionally MVNO differs from normal SPs of the hosting MNO only with regard to the scope and level of services In fact MVNO is not a virtual network operator, but an ESP of the hosting MNO.
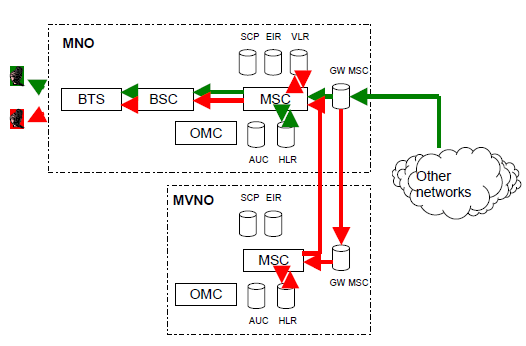
Figure 6: Call termination to MVNO's subscriber via the gateway-MSC of the hosting MNO and MVNO's MSC.
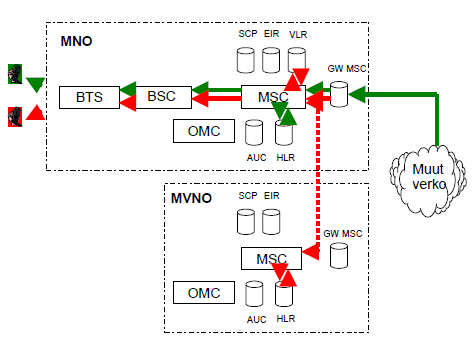
Figure 7: Call termination to MVNO's subscriber via the MSC of the hosting MNO.
Internal (on-net) traffic of MVNO
MVNO's internal, on-net traffic can be routed in two alternative ways:
- Switching the call in the MVNO's mobile switch MSC or
- Switching the call in the switch of the MNO.
Switching the call in MVNO's switch
Call is routed from MVNO's subscriber via MNO's BTS, BSC and MSC to MVNO's MSC. Call is switched in the MVNO's MSC and routed then back to MNVO's other subscriber, figure 8.
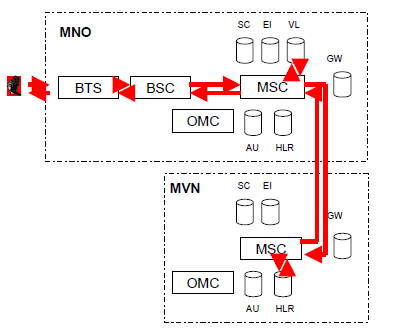
Figure 8. MVNO's internal call switched in its own MSC.
According to the way the call is using the network components, the cost of MVNO's internal call is higher than the cost of an internal call of the hosting MNO due to overlapping use of MSC. The cost of MSC functions is marginal compared with costs of radio access, therefore difference in costs of internal calls of MNO and MVNO is not significant.
Switching the call in the switch of an MNO
MVNO's on net call can be switched also in MNO's mobile switch. MVNO's own switch is updated by signalling, figure 9.
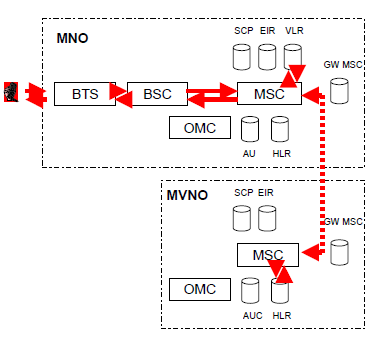
Figure 9: MVNO's internal traffic switched in MNO's switch.
According to alternative in figure 9, the usability of MVNO's own value added services may be difficult.
Traffic between MVNO and other network operators
Traffic between MVNO and its hosting MNO can take place in two alternative ways:
- Call is switched in the MVNO's mobile switch (call is routed via the point of interconnection) or
- Call is switched in the MSC of the hosting MNO (call is not routed via the point of interconnection).
Switching a call in the MSC of an MVNO
A call is routed through the point of interconnection between the MSCs of both the MNO and the MVNO, figure 10. This is a normal call conveyance procedure between two network operators. Termination charges are collected in both call directions, from MNO to MVNO and from MVNO to MNO.
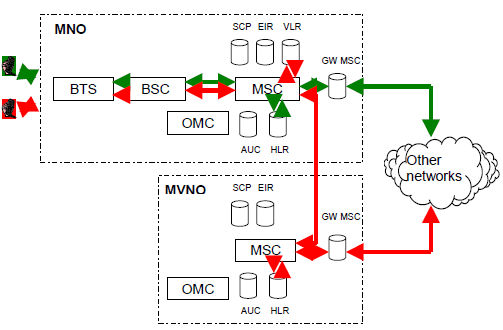
Figure 10: Call between MNO and its MVNO through their point of interconnection.
The cost of a call is a cost of call origination of MNO (MVNO) plus a cost of call termination of MVNO (MNO) plus a transit cost between the two networks.
Switching a call in the MSC of an MNO
In this alternative, a call is switched in the MSC of an MNO. It is not routed via the point of interconnection of the two networks, figure 11.
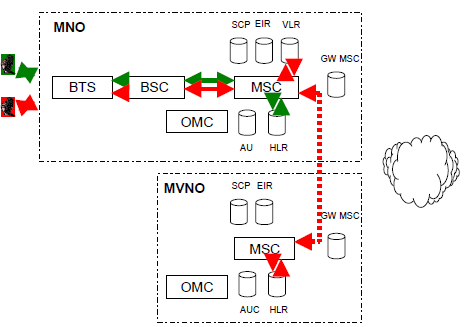
Figure 11: A call between MNO and its MVNO. Call is switched in the MSC of the MNO.
In this alternative, call does not go through the point of interconnection and termination charges are not paid. The cost of a call corresponds approximately to the cost of an internal call of the MNO.
Traffic between MVNO and other MNOs
Traffic between MVNO and other mobile networks flows always via the point of interconnection of the networks. Referring to the alternative 2 in section 5.3.1.2, other mobile operators are in unequal position to MVNO and its hosting MVNO: in traffic between the MVNO and hosting MNO, no interconnection charge is collected, in traffic between the MVNO and other mobile operators and in traffic between hosting MNO and other mobile operators, termination charges are collected, figure 12.

Figure12: Traffic between MVNO/MNO and other mobile operators.
